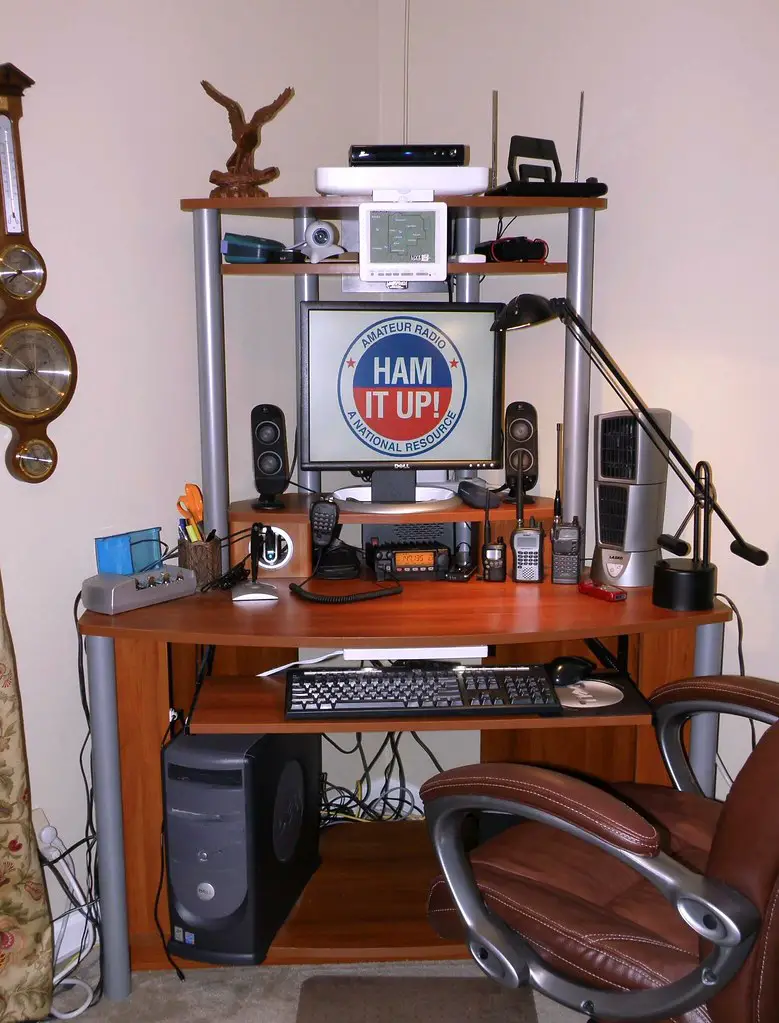
Many people find ham radios, also known as amateur radios, fascinating. They want to learn how to make one. Here’s the step-by-step process:
- You need a transceiver. It converts voice and data into electromagnetic waves and transmits them. Pick one that fits your needs.
- You also need an antenna. It captures signals from the air and sends them to the transceiver. Get an antenna that works with the frequencies you want.
- Power sources like batteries or a power supply unit are necessary too.
- Now connect the antenna and transceiver. Use coaxial cables or other suitable connectors. Make sure they’re secure.
- Test your setup before going on air. Check for secure connections and loose ends.
Make your ham radio! It’s rewarding and combines technical expertise and accomplishment. Explore this hobby and connect with people. Get going and unleash your inner radio enthusiast!
Understanding Ham Radio
Ham radio, also known as amateur radio, is an amazing hobby. It lets people communicate wirelessly around the world. To do this, they use radios often made by the operators, to send and receive signals. Here are five points to help you understand it better:
- Licensing: To legally operate a ham radio, you need a license from your national regulator. This makes sure operators know radio tech and regulations.
- Frequency Bands: Ham radios work on frequency bands for amateur radio use. You can use them for voice, Morse code, digital data, and satellites.
- Emergency Comm: An important part of ham radio is its use in emergencies. During disasters or when traditional networks fail, ham operators help aid organizations and communities.
- Experimentation: Ham radio enthusiasts can experiment with antennas, kits, and digital tech. They try out new techniques to push the boundaries of wireless communication.
- Community and Collaboration: Ham radio operators have a great sense of community. They take part in contests, events, and public service activities to make international friendships.
Ham radio has a long history that goes back over a century. There are countless stories of remarkable experiences of operators worldwide. For example, Bob is from a rural area without good internet or cell phone coverage.
During bad weather, Bob’s ham radio became a lifeline for his community. He worked with local authorities and sent emergency messages, making sure help got to those who needed it. Bob’s dedication as a ham radio operator shows how important it is in times of crisis.
Equipment Needed
To equip yourself for ham radio, you will need specific tools and resources that facilitate effective communication. The essentials for setting up a ham radio station include:
- Transceiver: This device serves as the central component of your ham radio station, enabling you to both transmit and receive signals.
- Antenna: A well-designed antenna is crucial for efficient signal transmission and reception. Consider factors like frequency range, height, and location when selecting an antenna that suits your needs.
- Power supply: A reliable power source ensures the uninterrupted operation of your ham radio station. Opt for a stable power supply, such as a battery or generator, that can withstand extended usage.
- Coaxial cable: This cable facilitates the transfer of signals between your transceiver and antenna. Choose a high-quality cable with proper shielding to minimize signal loss and interference.
- License: Obtain the necessary license from your country’s regulatory authority to legally operate a ham radio station. Compliance with regulations demonstrates proficiency in operating radio equipment and understanding of communication protocols.
It is essential to be aware of the unique details associated with setting up a ham radio station, such as ensuring proper grounding for your equipment and employing effective communication techniques. By making use of reliable equipment and adhering to regulations, you can embark on an exciting journey into the world of ham radio.
Embark on your ham radio journey today and unleash the power of communication. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to connect with fellow enthusiasts and explore the vast possibilities of ham radio. Start building your station and experience the thrill of worldwide communication. Join the global community of amateur radio operators and become a part of a truly remarkable hobby.
Get ready to tune in and amplify your ham radio skills with a radio transceiver that makes staying connected more enjoyable than getting sucked into a black hole.
Radio Transceiver
A radio transceiver is a must-have for effortless communication. It’s used to transmit and receive radio signals, making it an essential tool for staying in contact over long distances.
Known for its versatility, the radio transceiver has a wide range of features. Its frequency range is 136-174 MHz, giving you access to multiple channels. Also, its power output capability of 5W/1W ensures clear transmission in any environment.
Don’t miss out on the advantages of a top-notch radio transceiver. Whether you’re an outdoor enthusiast, part of a security team or working in emergency response operations, this device is crucial for successful communication. Invest in a reliable radio transceiver and enjoy improved connectivity and peace of mind.
Antenna
Antennas are essential devices for transmitting and receiving signals through high-frequency electromagnetic waves. They are vital for wireless communication systems, facilitating the transfer of information over long distances.
There are various types of antennas used: Dipole, Yagi, Parabolic, and Patch. Each has its advantages and drawbacks, depending on the application.
Plus, antennas can send and receive signals in different forms – radio waves, microwaves, and even light waves!
So, don’t miss out on investing in quality antennas for reliable signal transmission and reception. Stay connected and enjoy wireless communication!
Power Source
Power sources for electrical systems are essential. They provide the energy needed to run various devices and equipment. It’s important to choose a reliable source for seamless operation.
Here are the different types of power sources commonly used:
- Electrical Grid: A network that delivers electricity.
- Batteries: Portable energy storage.
- Generators: Engines or turbines that generate electricity.
- Solar Panels: Cells that capture sunlight and generate electricity.
- Wind Turbines: Mechanical devices that turn wind into electricity.
When selecting a power source, consider the specific requirements of each device. Some need a steady supply, while others are battery-powered.
To understand the development of power sources, look at their history. It all started with batteries in the 18th century. Later, power grids and renewable sources like solar panels and wind turbines emerged.
Setting Up Your Ham Radio Station
Setting Up Your Ham Radio Station:
Setting up a ham radio station requires careful planning and consideration. Follow these 6 steps to ensure a successful setup:
- Choose the right equipment: Select a reliable transceiver, antenna, power supply, and accessories based on your specific needs and budget.
- Find a suitable location: Set up your station in a place with minimal interference, such as a high location away from electrical devices and obstructions.
- Install the antenna: Depending on the type of antenna, mount it securely and position it for optimal signal reception.
- Connect the components: Use appropriate cables and connectors to link the transceiver, antenna, and other equipment. Ensure all connections are secure and properly grounded.
- Adjust settings and test: Tune the transceiver’s frequency and modulation settings, and perform necessary tests to ensure smooth operation.
- Obtain a license: Before using your ham radio station, obtain the required license from the appropriate regulatory authority in your country.
Remember, each setup is unique, so consult resources and fellow ham radio operators for specific advice.
In addition, it is important to be aware of local regulations about radio communication and transmission powers. Compliance with these regulations ensures the safe and legal operation of your ham radio station.
A True Story:
During a severe storm, a ham radio operator provided critical communication support when all other forms of communication were disrupted. His well-equipped and properly set up radio station allowed him to relay vital information, helping emergency services coordinate rescue efforts and aiding affected communities. The incident highlighted the significance of a well-prepared ham radio station in times of crisis.
Finding the perfect spot for your ham radio is like choosing a location for a secret underground lair, minus the evil genius plot…or maybe not.
Choosing a Location
When picking the place for your ham radio station, location is a top priority. Consider these must-haves:
- Access: Make sure the spot is easy to get to, so you can visit often and take care of maintenance.
- Interference: Look for a spot with minimal electronic or power-line disruption, for less noise and better performance.
- Antenna Placement: Your antenna needs height and line of sight, so nothing like tall buildings or trees blocks the signal.
- Power Source: You don’t want any surprising outages, so ensure a reliable power source.
Also, check out details like nearby emergency services or radio clubs, for help in case of emergencies or tech problems.
Before you start your ham radio journey, make sure you find the best spot. That way, you can communicate with other ham radio enthusiasts around the world!
Installing the Antenna
- Research is the first step when installing your antenna with precision. Find the best type for your needs and location.
- Gather materials like the antenna, coaxial cable, mounting brackets, and tools.
- Pick a spot that’s high, clear, and obstruction-free.
- Mount the brackets and attach the antenna, then attach the coaxial cable to the radio.
- Grounding is essential. Use rods and wires according to regulations.
- Lastly, use a SWR meter or analyzer to tune your antenna.
For extra help, look into feedline length and balun adjustments. Before installation, check local regulations and height limits. Also, keep any interference sources away from the antenna. An example of a tricky situation is a high-rise building in a busy city. Despite obstacles, planning and determination will help you reach out to fellow operators across long distances. Research, planning, execution, and overcoming obstacles are what it takes for a successful antenna installation.
Connecting the Equipment
A Pro Way to Connect the Gear:
When constructing your ham radio station, reliable connections are key. Here’s how to link your gear properly:
- Get a stable power source by plugging your radio equipment into a grounded outlet.
- Connect the transceiver and antenna using coaxial cables, for a secure fit.
- Link your computer or laptop to the transceiver with an audio interface cable for digital modes.
- For remote control capabilities, connect your transceiver to a router with an ethernet cable.
- Use appropriate connectors and adapters for any extra accessories you want to add.
Note these special steps while connecting the equipment. Keep cables neat and away from anything that could interfere, like power cords or fluorescent lights. Make sure to ground everything for safety. Double-check connections before switching on your ham radio station.
Now that you know how to link your ham radio equipment properly, don’t miss out on crystal clear conversations and exploring different types of communication. Get started now and unlock the exciting world of amateur radio!
Operating a Ham Radio
Operating a Ham Radio: The Professional Approach
When it comes to utilizing a Ham Radio setup, it’s important to understand the nuances of its operation. Here are three key points to keep in mind:
- Mastering Frequency Bands: Familiarize yourself with the different bands and frequencies assigned to Ham Radios, ensuring effective communication without signal interference.
- Proper Communication Etiquette: Learning and adhering to the established procedures and protocols for Ham Radio communication ensures clear and efficient transmission of messages.
- Operating Equipment Safely: Practice proper radio hardware handling, antenna installation, and power management to safeguard your equipment and yourself from potential hazards.
In addition, it’s crucial to explore other pertinent details such as antenna positioning for optimal reception and techniques to handle emergencies effectively.
Don’t miss out on the incredible potential that Ham Radio operation can offer. Start building your knowledge and skills today to fully experience the world of communication through amateur radio.
Learning the Lingo: Master the secret language of ham radio, where ‘CQ’ means ‘Hello’ and ‘QSL’ translates to ‘Did you get my last message or should I send it again? Because if you didn’t, we might have a problem called ‘communication’.
Learning the Lingo
Operating a ham radio has lots to learn! Mastering the terms used by ham radio operators is an important part of this. Knowing these terms lets you communicate easily and feel confident in the ham radio world.
A table of some common ham radio communication terms is here to help:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| CQ | An operator’s general call inviting others to contact them. |
| DX | Abbreviation for “distance” or “long-distance communication.” This gets operators excited! |
| QSL | A confirmation card is exchanged between operators as proof of contact. |
| Net | A scheduled gathering of hams, usually for training, on a particular frequency. |
| Ragchew | A casual and long chat between operators, usually about non-radio topics. |
| APRS | A system that lets hams send digital messages in real-time over the radio. |
These are just a few examples – there are lots more terms for all sorts of uses in ham radio.
To get comfortable with the lingo, try these tips:
- Go to local amateur radio clubs and organizations. Experienced members can help you understand ham radio language.
- Listen to conversations on different frequencies, to see how operators use terms in different situations.
- Read books about ham radio jargon and terminology. It’ll help you understand more and can be done at your own pace.
- Join online forums and discussion boards for amateur radio lovers. You can ask questions and talk to experienced operators.
By engaging with the ham radio community and learning more, you’ll feel more comfortable with the lingo and enjoy the ham radio experience even more.
Understanding Frequencies and Bands
Frequencies in Ham Radio range from low to high. Each band has its unique characteristics, great for specific distances and purposes.
Knowing frequencies and bands helps with things like propagation prediction software, antenna selection, and transmitter power adjustment.
I remember a time when my knowledge of frequencies was necessary. During a storm, traditional communication was down. I used my ham radio know-how to tune into a resilient frequency band. In minutes I had connected with emergency teams miles away.
This situation shows the importance of understanding frequencies and bands when using a ham radio. It’s not just a hobby; it can be used as a support system when other systems fail.
Operating Frequency Allocations in Ham Radio may seem intimidating. But with understanding, you unlock the potential for perfect long-distance communication and using the right bandwidths.
Making Contacts
Get ready to explore the world of ham radio communication! Here are six quick tips to help you make contacts:
- Build your network. Join local clubs and networks for advice on good frequencies and methods.
- Frequency hopping. Try different bands and modes like AM, FM, SSB, or digital.
- CQ calling. Use the universal call sign “CQ” followed by your call sign. Repeat this periodically while tuning.
- Connect through repeaters. Look for strategically placed repeater stations and listen for codes and tones.
- Embrace contests and events. Participate in organized activities for lots of contacts in a short time.
- QSL cards exchange. Send QSL cards as a token of appreciation and proof of communication.
Plus, keep in mind:
- The time of day affects propagation conditions.
- Adjust modulation, power, and antenna orientation for better clarity.
- Try moon bounce and satellite contacts for an extra thrill.
Making contacts with ham radio is about more than just tech stuff – it’s about building relationships and learning within the global ham community. Have fun and get on the airwaves!
Ham Radio Etiquette
Ham Radio Etiquette:
Ham Radio Communication Norms:
- Proper Identification: Every operator should identify themselves using their call sign at the beginning and end of each transmission.
- Respect for Others: Maintain courteous behaviour on the airwaves by refraining from using offensive language, making inappropriate remarks, or engaging in arguments.
- Listen before Transmitting: Before transmitting, take a moment to listen to ongoing conversations to avoid interrupting or causing interference.
Additional Considerations:
Operators are encouraged to remain mindful of signal strength and bandwidth usage to ensure optimal communication conditions. By adhering to these etiquette guidelines, ham radio operators create a positive and professional environment for all.
Pro Tip: Regularly brush up on existing and emerging etiquette practices to stay updated and maintain effective communication standards.
Remember, following proper protocols in ham radio is as important as not accidentally summoning aliens with your antenna.
Following Proper Protocols
Adhering to protocols in ham radio communication is essential for effective and efficient communication. By doing this, operators ensure their messages are delivered clearly and accurately, enhancing the experience for all participants.
To explain the importance of protocols, let’s look at these key aspects:
| Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Frequency Usage | Allocate frequencies to prevent interference and allow multiple conversations. |
| Call Signs | Use call signs at the start and end of transmissions to identify participants and ensure clarity. |
| Language | Use easy-to-understand language with minimal jargon. |
| Courtesy | Be polite and respectful towards other operators. |
Apart from these, it is important to listen before transmitting, keep transmissions concise, and monitor your signal strength. Also, use commonly-used Q-signals such as QSL or QRX to convey information efficiently and practice radio silence when there is nothing relevant to share.
By following these recommendations, you will increase the efficiency and effectiveness of your transmissions, and contribute positively to the overall flow of communication in the ham radio community.
Respecting Other Operators
Respecting other operators is critical in the world of ham radio communication. It guarantees a flawless and enjoyable experience for everyone involved. To uphold this, certain guidelines must be followed.
| 1 | Listen Before Transmitting | Before transmitting, it’s essential to listen to ongoing conversations on the frequency. This helps avoid disrupting ongoing exchanges and shows respect for others. |
| 2 | Prevent Unnecessary Interference | Stop causing unnecessary interference by following proper operating procedures and keeping good radio practices. This incorporates using suitable output power and avoiding the overuse of repeaters. |
| 3 | Be Polite and Courteous | Always show politeness and courtesy towards other operators. Utilize clear and concise language, steer clear of offensive or inappropriate content, and treat others with kindness and respect. |
As well as these guidelines, bear in mind that every operator has different levels of experience and expertise. Some may be new to ham radio whereas others have years of experience. Bearing this in mind allows for an all-inclusive environment where knowledge can be shared openly.
To further boost respectful interactions, consider the following:
- Be patient with less experienced operators who may need guidance.
- Offer assistance when necessary, giving constructive feedback to help them improve their skills.
- Acknowledge and appreciate the contributions of fellow operators in creating a positive atmosphere.
By applying these suggestions, we create an environment that encourages companionship among operators while advancing continuous learning. Moreover, it adds to the general growth and development of the ham radio community as a whole.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Troubleshooting and Maintenance play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth functioning of a ham radio setup. Here are three key points to consider:
- Regularly inspect and clean the equipment to prevent dust accumulation and potential damage.
- Check for loose connections and inspect cables for any signs of wear and tear; replace them if necessary.
- Keep an eye on the antenna system and ensure it is properly tuned and aligned for optimal performance.
It’s important to note that taking these steps can help maintain the longevity and efficiency of your ham radio system. Now, let’s delve into some unique details.
When it comes to troubleshooting, it’s essential to have a systematic approach. Start by identifying the problem, followed by a step-by-step analysis of potential causes. Narrow down the possibilities through testing, and once the issue is pinpointed, take the necessary steps to rectify it. Problem-solving in a structured manner enhances the overall performance of the ham radio system.
Now, let’s share a true story that highlights the importance of troubleshooting in ham radio. One enthusiast experienced intermittent signal loss despite having a well-set-up system. Through systematic troubleshooting, they discovered a faulty coaxial cable connection. Replacing the flawed cable restored the efficiency of their ham radio operations, emphasizing the significance of regular maintenance and meticulous problem-solving.
Ham radio enthusiasts know that when their signal is weak, it’s not their love life they must fix, but rather their antenna.
Common Issues and Solutions
Facing tech issues with your system can be a drag. Here are some common problems and their fixes to help you quickly troubleshoot and repair.
Issue | Solution
- Slow performance | Clear temp files and optimize storage. Update software often for smooth running.
- Internet connection troubles | Reboot the router and check the settings. Switch off any VPNs or firewalls blocking the connection.
- System crashes or freezes | Update device drivers, scan for malware, and free up memory space. If the issue continues, reinstall the operating system.
- Printer not working | Check connections, restart printer and computer, update drivers, and check for paper jams or low ink levels.
- Software compatibility issues | Make sure the software is compatible with your OS. If not, look for an alternative program or upgrade to a compatible version.
- Hardware malfunction | Check connections, cables, and power supply. Replace faulty hardware or get professional help.
Besides these solutions, always keep your system up-to-date with the latest patches and security updates. It’s also wise to back up important files to avoid data loss in case of an emergency.
Follow proper maintenance practices like cleaning your device from dust, avoiding overloading it with unnecessary programs, and protecting it from extreme temperatures.
By following these hints and steps, you can save time and frustration. Plus, you’ll make sure your system runs smoothly. Stay ahead in keeping your technology in optimal condition!
Regular Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is essential to keep equipment running at its peak. Here are some tips to help you stay on track:
- Inspect and clean filters regularly – prevents clogging & boosts efficiency.
- Replace worn-out or damaged parts to maintain performance.
- Lubricate moving components – reduces friction & increases lifespan.
- Tighten loose screws, bolts, and connections – ensures stability & safety.
- Calibrate & test equipment – ensure accurate readings & reliable performance.
- Keep records of maintenance activities – dates, tasks done & issues encountered.
Plus, regular maintenance uncovers potential problems before they become costly! According to a [source name] report, businesses that prioritize maintenance experience less downtime & higher productivity.
Conclusion
Ready to explore ham radio? This hobby offers endless possibilities for communication and connection. Get started by investing in the right equipment: a transceiver, antenna, and power supply. Additionally, learn about frequency bands and licensing requirements.
Once you have everything, set up your station. Connect your transceiver to the antenna. Don’t forget height, directionality, and grounding. This will maximize your signal strength and minimize interference.
Explore different modes of operation like voice communication or digital transmission. Experiment with accessories like amplifiers or filters. Then, get ready to connect with fellow enthusiasts around the globe. You’ll also be prepared for crucial communications when traditional methods fail.
It’s time to build your ham radio setup! Embrace the challenge and unlock an incredible world of possibility.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQs on How To Make Ham Radio:
1. What is a ham radio?
A ham radio, also known as an amateur radio, is a communication device that allows individuals to communicate with each other over radio frequencies, usually for personal or non-commercial purposes.
2. What components are needed to make a ham radio?
To make a ham radio, you will need components such as a transmitter, receiver, antenna, power supply, and audio equipment. These components are essential for transmitting and receiving radio signals.
3. Is it difficult to make a ham radio?
While making a ham radio may require some technical knowledge and skills, it is not overly difficult. With proper research, planning, and guidance, it is possible for individuals with an interest in electronics to build their ham radio.
4. Are any specific regulations or licenses required to use ham radio?
Yes, to legally operate a ham radio, you usually need to obtain an amateur radio license from the appropriate governing organization in your country. These licenses ensure that operators understand the regulations and practices of ham radio operation.
5. Where can I find resources to learn how to make a ham radio?
There are numerous resources available online and in print that provide step-by-step instructions, circuit diagrams, and guidance on building ham radios. Online forums and communities dedicated to amateur radio enthusiasts are also valuable sources of information and support.
6. Can I modify or customize my ham radio after building it?
Absolutely! Many ham radio enthusiasts enjoy modifying their radios to suit their specific needs and preferences. However, it is essential to ensure that any modifications comply with relevant regulations and guidelines to maintain legal operation.